 Insect and spider bites can cause an allergic reaction. Stinging insects (such as bumblebees, yellow jackets, hornets, wasps, and fire and harvester ants) are more likely to cause an allergic reaction than biting insects (mosquitoes, horseflies, deerflies, spiders, bedbugs, and black flies).
Insect and spider bites can cause an allergic reaction. Stinging insects (such as bumblebees, yellow jackets, hornets, wasps, and fire and harvester ants) are more likely to cause an allergic reaction than biting insects (mosquitoes, horseflies, deerflies, spiders, bedbugs, and black flies).Most bites and stings do not require emergency medical care. However, approximately 0.5% of the population develop severe allergic reactions (anaphylaxis) to insect stings.
Allergic reactions to insect bites or stings occur very quickly, usually within minutes. Severe reactions, although rare, can be rapidly fatal if untreated.
Symptoms
Common symptoms include:
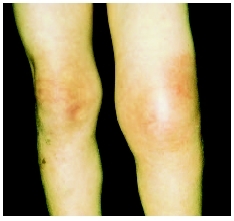
- Red, swollen, or warm lump
- Hives
- Rash
- Itching, tingling, numbness, burning, tenderness, pain
Serious allergic reactions (anaphylaxis) occur when symptoms spread. These can include difficulty breathing, dizziness, nausea, diarrhea, fever, muscle spasms, or loss of consciousness. Call for emergency medical help right away.

First aid for minor reactions
- If the sting is from a honey bee, remove the stinger from the skin if it is still present. Carefully scrape the back of a knife or other thin straight-edged object across the stinger if the victim can remain still, and it is safe to do so. Otherwise, you can pull out the stinger with tweezers or your fingers, but avoid pinching the venom sac at the end of the stinger which will cause more venom to be released.
- Wash the site thoroughly with soap and water.
- Cover the site with a clean, cold compress or a clean, moist dressing to reduce swelling and discomfort.
- Over the next 24 to 48 hours, observe the site for signs of infection (such as increasing redness, swelling, pain).
- Sores from scratching can become infected. Keep bites clean and, to prevent infection, don't scratch.
First aid for serious reactions

If the victim is having a severe reaction or the victim has been stung inside the mouth or throat, call immediately for emergency medical assistance.
- Check the victim’s airway, breathing, and circulation. If necessary, begin rescue breathing and CPR.
- Reassure the victim. Try to keep him or her calm, as anxiety will worsen the situation.
- Remove nearby rings and constricting items because the affected area may swell.
- Use a special allergy first aid kit, if available. (Some people who have serious insect reactions carry it with them.)
- If appropriate, treat the victim for signs of shock. Remain with the victim until medical help arrives.
|
Bookmark this post:
|
|

0 comments
Post a Comment